Concussions — a form of injury to the brain — are common and are usually not life threatening, though their symptoms can sometimes be serious or lead to more serious conditions. But what are the symptoms of a concussion, and how should you treat one?
In most cases, concussions can be treated at home with plenty of rest. However, they are still injuries and should be treated with care. The brain needs time to heal after even a minor concussion occurs, and signs of more serious effects may not appear until later.
If the symptoms are severe, don’t get better after a few days, or get worse over time, the person may need emergency medical care. If you suspect you or someone you know has a concussion, monitor their symptoms closely and consult a doctor on how best to treat the injury.
So what are the symptoms of a concussion, and how do you know if a head injury needs emergency care? Here’s what you need to know about recognizing and treating concussion symptoms, and preventing future head injuries.
What Is a Concussion?
The CDC defines a concussion as “a type of traumatic brain injury—or TBI—caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head or by a hit to the body that causes the head and brain to move rapidly back and forth.”
A concussion may occur during a sports match or practice, as a result of a vehicle accident or fall, or in any other situation where a person’s head and/or neck suffers trauma. While concussion symptoms are usually temporary and not life-threatening, their effects can still be serious.
In the past, people have categorized concussions into three “grades” of severity, where a grade 1 concussion was considered the most mild, and a grade 3 was considered the most severe. This is only one of several grading systems that have been used to determine the severity of a concussion and the treatment it requires.
However, experts now recommend evaluating every concussion on an individual basis. Some concussions may appear mild at first, only for more severe symptoms to appear later. Additionally, classifying a concussion as “mild” may allow the person to fully return to their typical activities such as sports before the injury has healed, putting them at risk of further injury.
Because research on concussions is still emerging, it’s always best to play it safe. If you or someone you know has suffered a concussion, and you aren’t sure about the severity of the injury, consult a doctor and monitor the symptoms carefully.
What Are the Symptoms of a Concussion?
Concussion symptoms can vary greatly depending on the person, their medical history, and the circumstances of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Headache
- Confusion
- Temporary memory loss (especially of the concussion-inducing event)
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Ringing in the ears
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness or blurry vision
While some people may temporarily lose consciousness from a concussion, not everyone will. A concussion can still have severe effects even if there is no loss of consciousness.
Other symptoms, such as changes in mood or irritability, difficulty concentrating, or increased sensitivity to light, may appear later and last for a longer period of time than other symptoms.
How Do You Identify a Concussion?
Anyone who has experienced a blow, bump, or jolt to the head should be checked and monitored for signs of a concussion. Only a healthcare professional can diagnose a concussion, but you can check for common symptoms like those listed above.
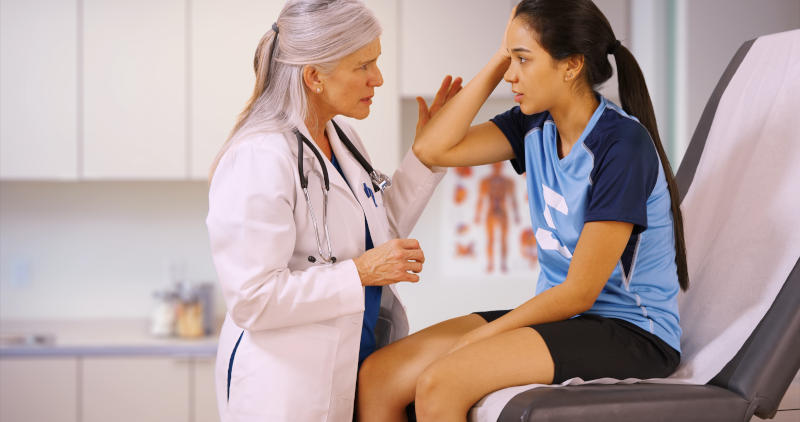
Additionally, a concussion test can help assess the person’s alertness, memory, and other brain functions that could be affected by a concussion. These tests can range from asking a few simple questions to complex questionnaires. Some tests can be conducted at home, while others are done in a medical facility.
However, while these tests can be useful for gathering information, they should not be used as a substitute for a medical diagnosis. You should still see a doctor for specific advice on treating any kind of head injury — even if it doesn’t seem severe at first.
When Do Concussion Symptoms Start?
Just as answers to the question “What are the symptoms of a concussion?” can vary greatly, there is no simple answer to the question “How long after hitting the head can concussion symptoms start?”
Sometimes, symptoms of a concussion start immediately after the injury. However, other times they may not appear until hours or even days later. If you suspect that you or someone you know may have a concussion, even if no or few symptoms are present, it’s always best to see a doctor within a day or two.
If the injury occurred during a sports match, do not allow the athlete to return to play, even if there are no obvious concussion symptoms yet. The last thing you want is for them to sustain a second head injury before the first has healed, or for mild concussion symptoms to worsen.
How Long Can Concussion Symptoms Last?
With plenty of rest and care, mild concussion symptoms may only last a few hours, and should not last longer than a few days at most. Symptoms that last longer than several days or that get worse instead of better can be signs of complications that require medical attention.
However, keep in mind that no head injury — no matter how minor it seems — should be taken lightly. When in doubt, consult a doctor, especially before resuming strenuous activities.
How Do You Treat a Concussion?
How to treat a concussion depends on the person and the severity of their injury, and should be evaluated on a case-by-case basis. While concussion symptoms are often mild and may not always require a doctor visit, they can sometimes lead to more serious, long-term effects, especially if not given adequate rest.
How to Treat a Mild Concussion
If the concussion and symptoms are mild, the best treatment is getting plenty of rest and monitoring for severe or worsening symptoms. The injured person should temporarily avoid playing sports, driving, or other activities that put stress on the brain so as to give it time to heal.
It’s not necessary to keep the person awake for a certain amount of time after they experience a concussion. However, difficulty or inability to wake up following a concussion can be signs of a more serious injury, so it’s often recommended to wake the person after a few hours.
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen can also help alleviate concussion symptoms, but avoid anti-inflammatory medications like aspirin or ibuprofen, which can increase the risk of internal bleeding.
How to Treat Serious or Worsening Concussion Symptoms
Symptoms of a mild concussion typically improve after a few hours or days, so if the person’s symptoms last longer — or if they get worse instead of better over time — this can be a sign of a more serious injury that requires medical attention.
A person who has experienced a concussion should also see a doctor if the symptoms are severe, or if they have had multiple concussions in the past. In some severe cases, surgery or other medical treatment may be necessary.
So what are the symptoms of a concussion that may indicate a severe injury? Serious concussion symptoms can include, but are not limited to:
- Difficulty waking up
- Seizures
- Slurred speech
- Loss of consciousness
Remember, no two concussions are the same. Some severe concussion symptoms may not appear until much later, and others — like loss of consciousness — may not occur at all, even in the case of a more severe concussion.
How to Treat A Concussion in a Child
Like adults, children who experience a concussion can show symptoms either immediately or after some time has passed. However, very young children may not be able to express what symptoms they are experiencing. Carefully monitor the child for signs of serious effects, and ensure they get plenty of physical and mental rest.
To ensure the child gets enough mental rest, you may need to request accommodations from their school as recommended by the child’s healthcare provider. Do not allow them to participate in sports or other physical activities until their doctor has approved for them to do so.
How Can You Prevent Future Concussions?
Since a concussion is typically caused by an impact to the head or upper body, one of the best ways to prevent concussions is to take proper safety precautions — like wearing a helmet — when participating in activities that have increased potential for head injuries to occur.
Other safety measures might include:
- Securing the home environment: Clear and maintain walkways, stairways, and other high-traffic areas in the home to minimize the risk of falling. This is especially important for elderly people who live alone.
- Following traffic laws: Whether you use a car, bicycle, motorcycle, or any other type of vehicle, take care to follow safety regulations and stay alert at all times.
- Practicing awareness: Both at home and when you’re out and about, be aware of your surroundings. Accidents can happen anywhere, and are often out of our control, but sometimes just staying aware of what’s going on around you can help you avoid falling or being hit by people or objects.
Of course, no amount of precautions are 100% effective at preventing accidental injuries. But by taking these precautions, you can reduce your chances of suffering a concussion or other similar injuries.
Finally, if you have already experienced a concussion, you can prevent further injury by monitoring your concussion symptoms and refraining from overexerting yourself before you have fully recovered.
What Is Second Impact Syndrome?
A rare but extremely dangerous event that can follow an untreated concussion is second impact syndrome, a rapid swelling of the brain resulting from a second concussion that occurs before the first has fully healed.
Second impact syndrome can set in very quickly and is usually fatal — sometimes within a few minutes. People who do survive are often permanently and severely disabled.
Like with concussions, second impact syndrome symptoms can initially appear less serious than they actually are. Even a minor impact can trigger the event and cause an otherwise healthy person to collapse after seeming to be uninjured moments before.
This is why it’s so important to prevent someone who has experienced a concussion from returning to strenuous activities too quickly. An athlete may be disappointed at not being able to finish the game, but that’s far better than them sustaining a second concussion and dying or being disabled for life because of second impact syndrome.
A person who has sustained a second head injury — whether there are signs of a concussion or not — should receive immediate emergency care and be checked for brain swelling, bleeding, or other damage.
Treat Concussions with Care
While answers to the question “What are the symptoms of a concussion and how do you treat one?” can vary widely depending on the circumstances of the injury, concussions are often mild and temporary. However, in some cases, more serious complications or symptoms can still appear after the fact.
It is important to take preventative measures to protect yourself and your loved ones from head injuries, and to carefully treat any head injuries that may occur. In some cases, severe injuries can appear harmless at first, and sustaining a second concussion before the first has healed can be devastating.
For more safety tips and first aid training, follow us on LinkedIn.